Dataset Description
In this paper, we used the “UCTH Breast Cancer Data Set” for machine learning analysis. Patient data was uploaded in 2023 to a trusted repository called Mendelly Data17. Obtained by observing 213 patients over two years by observing 213 patients from Calabar Teaching Hospital, Nigeria. It included nine features of age, menopause, tumor size, involved nodes, breast area, metastasis, quadrant-affected cancer history, and diagnostic results. Age and tumor size are continuous variables. Menopause, involved nodes, breast, metastasis, breast quadrants, and history are categorical variables. The categorical target variable is “diagnosis results”, which include “0” for benign and “1” for malignant diagnosis. Table 2 provides a comprehensive description of the features within the dataset.
Statistical preprocessing
This study used Jamovi to draw statistical and descriptive conclusions.18. Descriptive analysis of continuous variables is shown in Table 3. A violin plot is shown in Figure 2 to visualize the distribution of numerical data. According to the plot, older women are more likely to develop malignant breast tumors than younger women. Larger tumor size indicated a malignant diagnosis. The t-test was used to confirm the importance of continuous function. This feature is considered important if the p-value is less than 0.001. From Table 4, it is concluded that both tumor size and age are required features.
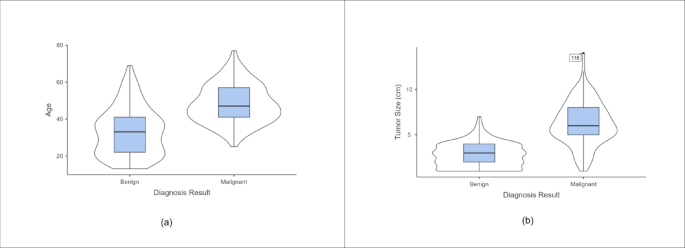
Violin plot. (a) Year (b)Tumor size.
Categorical variables are analyzed using the bar plot shown in Figure 3. We showed the number of patients with benign and malignant tumors for different characteristics. From the graph, breast cancer is interpreted as not harmful in patients who have not reached menopause. This cancer diagnosis is also observed when the tumor spreads to the auxiliary node. Metastasis has been observed to be prominent in breast cancer. It has been reported when malignant tumors affect the upper lateral quadrant. Patients with a previous history of cancer are more likely to be diagnosed with this cancer. These bar plots help you to analyze your dataset in detail. A chi-square test is performed to identify important category features. The results are shown in Table 5. Characteristics: Menopause, involved nodes, breast quadrants, and metastases are inferred as required attributes according to the chi-square test.
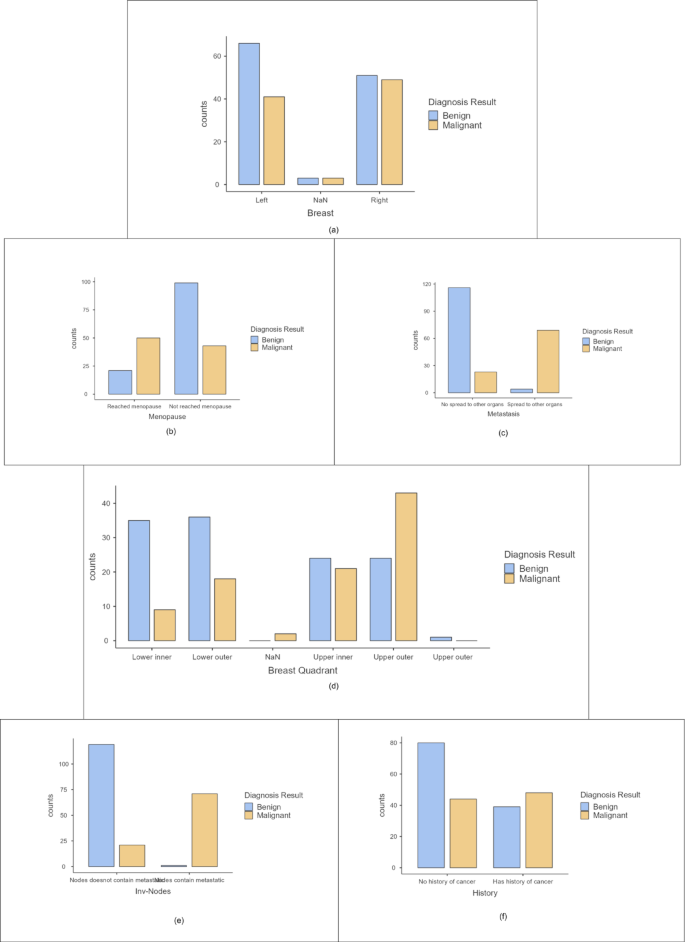
Bar plots for categorical variables (a) chest (b)menopause(c) metastasis (d) Breast quadrant (e)Related nodes (f) history.
Data Preprocessing
Data preprocessing allows raw data to be converted into an easy-to-read format and used for analysis. In this study, pre-processing was used to avoid using missing and outliers and to optimize the input function size during analysis. Shuffling of data was first done to prevent models from recalling orders. The dataset had 13 null values, represented as “Nans”, which were later removed to achieve uniformity. Because machine learning algorithms require numerical input, we converted categorical text data to numbers using label encoding. Assign each category a separate integer that the machine learning algorithm can handle. Data scaling avoids bias for larger values in the dataset. I converted all numbers between 1 and -1 using the maximum absolute value using MAX-ABS scaling.
The correlation between mutual information and Pearson is used to determine important features. The correlation coefficients between any two sets of characteristics are displayed as heatmaps of Pearson's correlation matrix. Values 1,0 and -1 indicate positive, zero, and negative correlations, respectively. The heat map is shown in Figure 4. This showed that the nodes involved, metastasis, tumor size and age were highly correlated with the diagnosis results. Mutual information is a univariate filtering method in which the importance of a function is calculated individually. It shows the dependency between two variables with the concept of entropy. In Figure 5, quality is ordered in order of importance. Mutual information suggests that key features involve nodes, tumor size, metastasis, age, menopause, breast quadrants, and history. Visualization of the distribution of target variables (diagnostic results) is shown as a pie chart in Figure 6. The diagram shows that there is a slight imbalance in the data. Borderline small is applied to training data that balances the class by creating synthetic samples. This has resulted in a 50% balance of datasets in both cases19. Furthermore, the dataset was split into test and training data at a rate of 30:70.
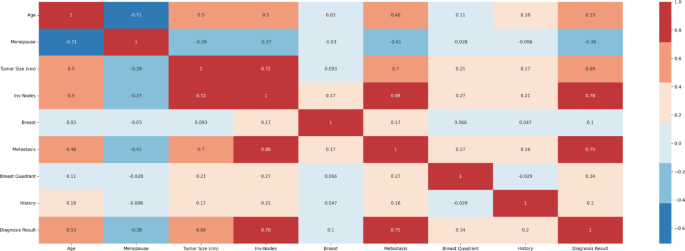
Pearson correlation heat map.

Mutual information about the functions.

Machine learning and explainable artificial intelligence
This study employs multiple machine learning classification techniques and combines these classifiers using stacking algorithms. The eight classifiers used are xgboost, lightgbm, catboost, adaboost, knn, decision tree, logistic regression, and random forest. They use different approaches, but xgboost, lightGBM, catboost, adaboost, and random forests integrate multiple tree models to improve performance. Decision Trees, Logistic Regression, and K-NN work without combining multiple models. LightGBM and XGBoost are great for speed and performance. The output from the above classifier is trained in the metaclassifier by a stacking algorithm. The stacking methodology is to improve model performance by integrating the unique strength of each base model and reducing overfitting. It also trains on predictions from the base model, which enhances generalization. This alleviates any noticeable bias and error in any model. The architecture for this is shown in Figure 7. Hyperparameters are set prior to training to control how the model is trained. It is performed to determine an ideal set of hyperparameters to optimize model performance and generalize the learning process to respond well to invisible data. GridSearchCV is used for adjusting hyperparameters using 5x cross-validation in this study. A detailed flow chart of the following methodology is shown in Figure 8.

XAI techniques improve model performance, interpret results, and provide transparency in model predictions. The Need for XAI: Improve model reliability by identifying the cause of misclassification. It provides transparency to your models. This helps doctors understand the rationale behind treatment in decision making. It also helps to identify important features for breast cancer detection. This study used five Xai technologies: Shap, Lime, ELI5, Qlattice, and Anchor. Shap (Shapley Additive Description) is a method of interpreting complex machine learning models that assign important values to each feature known as Shapley values. These values measure the effect of each input attribute on the model's predictions20. Provides detailed and individualized explanations for both physicians and patients. The contribution of individual functions is important in improving the model by identifying unexpected functional interactions. Shap is a combination of different models, a model and dependency that can be applied to any machine learning model, in this case any machine learning model on the stack. Lime (locally interpretable models and existing descriptions) is an agnostic model that explains the local environment of a sample.twenty one. We modify small aspects of the data to observe the impact of change on predictions, thus facilitating identification of the most relevant features. It is especially useful for scenarios that involve predictions for specific patients. Provide transparency at an individual level. Lime offers flexibility across a variety of models without changes like SHAP. Lime provides explanations that are easy for patients and non-technical stakeholders to understand. Using ELI5 (I'm explaining like 5 people) allows you to explain classifier weights and predictions. Provides global and local descriptionstwenty two. By analyzing the contributions of various features to model prediction, ELI5 helps identify biases that may have been incorrectly introduced during the model training process. Understand the internal mechanisms of the model and help troubleshoot existing issues. For example, if the model disproportionately weighs unrelated features, it could indicate overfitting or data quality issues. This is a user-friendly interface and is the best option for text data, like this study. It provides insight into the behavior of complex models by explaining how input text elements affect model predictions. qlattice Explanationability is a technique for searching for data patterns and connectionstwenty three. Rather than simply fitting the data to a given model, we investigate a wide range of alternative models that provide an understanding of the relationships of the data. A Qlattice model is a set of mathematical formulas that allow outputs and inputs to be connected via infinite spatial pathstwenty three. Unlike many machine learning models, Qlattice focuses on finding simple, interpretable expressions for users to understand how inputs are converted to output, making the model inherently transparent. It identifies key features and provides information about how they interact with each other to influence outcomes. It is robust to new data as it can be adapted by exploring new models and adapting to changes in data patterns. The anchor is also a model-independent interpretation created by Marco Tulio Ribeiro. Use if-then rule known as anchortwenty four. In a medical diagnosis, the anchor may specify that the diagnosis is always in a specific condition when certain symptoms and test results are present. It explains a particular decision by identifying key factors that have a significant impact on it. Even if the overall model behaviour is complex and nonlinear, it explains exactly why a particular decision was made and stays locally faithful. This method helps users develop reliability in their models by outlinening the justifications of each prediction. Table 6 provides an overview of the characteristics of the Xai technology used. Various techniques increase the reliability and versatility of interpretive output through mutual evaluation of explanations. The Xai technology in this study complements each other in terms of speed, adaptability and ease of interpretability for physicians and patients. Because of the different insights in the model's decision-making process, integrating all five methods will leverage unique strengths.
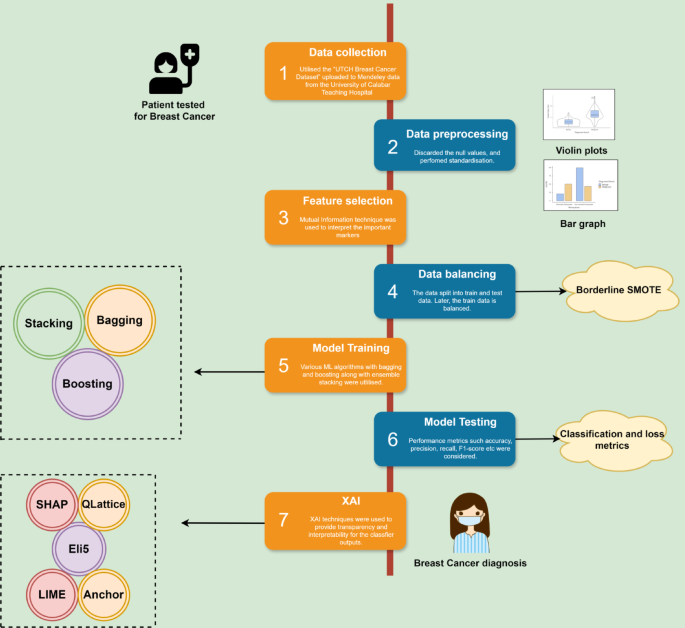
Flow diagram-based methodology.




