Author: Priority Research
Mayo Clinic has introduced a new artificial intelligence tool that can detect nine types of dementia using a single brain scan. This innovation can significantly improve the process of dementia detection, eliminating the need for human interventions and other devices. A tool named “StateViewer” identifies nine different patterns associated with symptoms of dementia and uses a single efficient brain scan to manifest itself as a disease such as Alzheimer's disease.
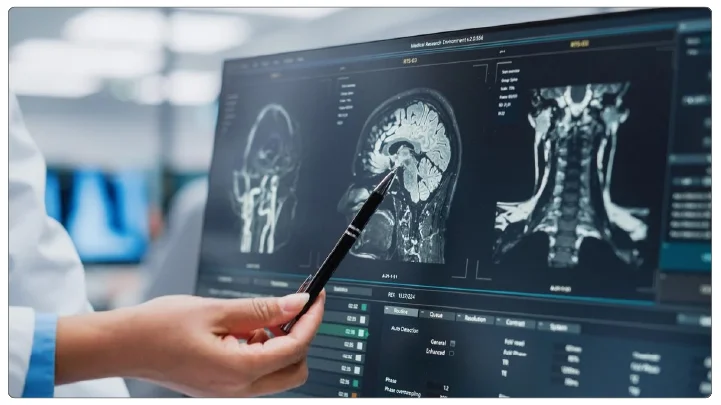
A study published in the Journal of Neurology shows that Stateviewer accurately identified different types of dementia in 88% of cases. Compared to traditional brain scanning methods, this AI tool can speed up the scanning process twice as fast as it is highly accurate, helping doctors to effectively identify and analyze data. To achieve this, researchers trained AI tools using nearly 36,000 brain scans from patients with normal cognitive function and individuals with dementia. This huge dataset allows AI tools to accurately compare how a healthy brain looks with the brain affected by dementia and its associated symptoms. What's even more interesting is that StrateViewer utilizes popular imaging techniques that provide advanced diagnostic support without the need for a neurology team.
Dementia affects people worldwide, with nearly 55 million and 10 million new cases being identified each year. Finding robust solutions to detect these diseases in the early stages becomes essential. According to Dr. David Jones, neurologist and director of the Neurological Artificial Intelligence Program at Mayo Clinic, “Every patient who steps into my clinic carries a unique story shaped by the complexity of the brain, which draws to neurology and continues to promote a commitment to clear answers.
This tool analyzes fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) scans. Using this scanning method, by disrupting these glucose molecules, the brain can detect how glucose is used to derive energy. This data is then compared with data from people who identified differences, further aggregating the types and combinations of dementia. Stateviewer displays these patterns through color-coded brain maps, highlighting brain activity in key areas associated with dementia. Researchers at Mayo Clinic plan to further expand the use of the tool to achieve high scalability.




