Artificial Intelligence Governance is a legal framework to ensure that AI and machine learning technologies are researched and developed with the aim of helping AI and machine learning technologies adopt and use these systems in an ethical and responsible way. AI governance aims to bridge the gap that exists between accountability and ethics in technological advancements.
AI use is rapidly increasing in almost every industry, including healthcare, transportation, retail, financial services, education, and public safety. As a result, governance plays an important role and is attracting attention.
The main focus of AI governance lies in AI. In terms of how it relates to justice, data quality, and autonomy. Overall, AI governance determines how well it can shape the algorithms of everyday life and how AI capabilities can be monitored. Some key area governance addresses include:
- Safety and misuse of AI.
- A sector suitable for AI automation.
- Legal and institutional structures regarding the use and technology of AI.
- Control and access to personal data.
- Moral and ethical questions related to AI.
- AI bias.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wp6z_x5d-rw
Why is AI governance necessary?
AI governance is necessary when machine learning algorithms are used to make decisions, especially when those decisions can have a negative impact on humans. For example, AI governance determines how best to handle scenarios where AI-based decisions can become unfair or breach human rights. Machine learning bias can incorrectly identify basic information about users, particularly in terms of racial profiling. This could unfairly deny individuals access to medical care and loans and mislead law enforcement in identifying suspected criminals.
The rapid adoption of AI tools, systems and technologies in a variety of industries also raises concerns about AI ethics, transparency and compliance with other regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Without proper governance, AI systems can pose risks such as biased decision-making, privacy violations, and data misuse. AI governance seeks to promote the constructive use of AI technology while protecting user rights and preventing harm.
Pillars of AI Governance
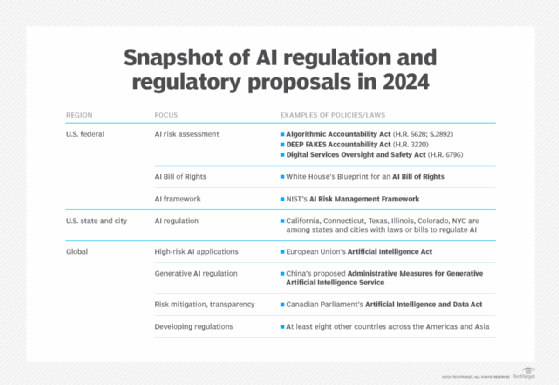
The White House Department of Science and Technology has created a blueprint for the AI Bill of Rights, which outlines a collection of five guidelines and practices regarding the design, deployment and use of AI systems. The goal of this blueprint is to help protect the rights of American citizens when it comes to using AI. These principles include:
- A safe and effective system. This principle indicates that AI systems should not be thoroughly tested and monitored to ensure they are safe and functioning as intended, and that they should not be designed in any way that could put individuals at risk.
- Algorithm discrimination protection. The principle states that AI systems should not exhibit unfair discrimination based on race, color, ethnicity, gender, religion, age, nationality, or other classifications protected by law.
- Data privacy. This principle states that individuals need to control their data and should be protected from abusive data practices using built-in protection.
- Notifications and explanations. This principle states that individuals need to know when AI or automated systems are being used and be informed about how it works.
- Human choices, considerations, fallback. The principle states that individuals should be able to opt out of using AI or automated systems in favor of human alternatives when necessary.
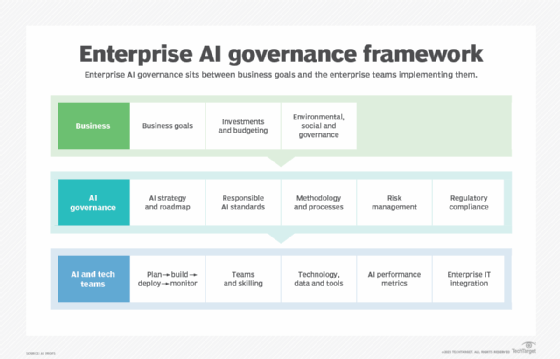
Other components of the powerful AI governance framework include:
- innovation. It promotes business and science efforts to leverage and optimize the benefits of AI.
- Trustworthy AI. Ensuring that AI is transparent and does not violate civil liberties, the rule of law, or data privacy.
- Education and training. Encourage the use of AI to expand opportunities and access to new employment, industry, innovation and education.
- Infrastructure. It focuses on expanding ethical access to data, models, computational infrastructure and other infrastructure elements.
- International cooperation. fostering international collaboration and partnerships built on evidence-based approaches, analytical research and multi-stakeholder engagement.
- decision making and explainability. The ability to understand the explanationability, or the reasons behind AI outcomes, is important to building trust and accountability.
- Regulatory compliance. Organizations must adhere to data privacy requirements, accuracy standards, and storage restrictions to protect sensitive information. AI regulations help protect user data and ensure responsible use of AI.
- Risk management. AI governance ensures responsible use of AI and effective risk management strategies, including selecting the right training data set, implementing cybersecurity measurements, and addressing potential biases or errors in AI models.
- Stakeholder engagement. Attracting stakeholders, such as CEOs, data privacy officers, users, and more is essential to effectively manage AI. Stakeholders contribute to decision-making, provide monitoring, and ensure that AI technology is developed and responsibly used throughout the lifecycle.
How organizations approach AI governance
There are many actions that an organization can take to implement effective and sustainable AI governance practices. They include:
- AI culture. Everyone in an organization should feel that they have a role to play in AI governance. This process occurs over time and requires training programs for employees to be able to form a continuous learning culture around AI governance.
- communication. In particular, employers should always communicate employees and the risks of poor governance AI systems.
- AI Governance Committee. Establishing an oversight and governance committee with members with expertise in this field will help the organization adhere to AI policies.
- Continuous improvement. By using AI tools and systems to gather feedback from employees and customers, organizations can continuously improve their AI applications and products. It is also important to continuously monitor AI usage and identify and fix issues.
- risk assessment. Third-party organizations specializing in AI risk assessment and auditing can provide another perspective on how to improve AI use and governance and minimize the associated risks.
- Governance metrics. Metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) allow you to verify that your organization is complying with AI governance policies. It is also important to monitor and manage these policies over time, as AI can deteriorate over time. AI KPIs are quantitative or qualitative and should include not only data security, financial value, and algorithm bias, but also measures source, truthfulness, and data quality.
- Environmental impact. The process of training and running AI over time can have a major impact on the environment. Organizations need to take care and make every effort to mitigate the impact on the environment.
What is AI Model Governance?
AI Model Governance is a subset of AI Governance, particularly involving the way organizations develop and use AI and machine learning models safely and responsibly. Organizations developing and using these models must have the following considerations:
- Ownership of the model. AI development usually involves a team of people working on the model. Tracking the work that each team member completes is key to ensuring model success, improving collaboration, and avoiding issues such as unnecessary duplication.
- Rules and regulations. By implementing a set of rules, aspects of model development, such as data quality, functional engineering, and documentation, are error-free and compliant with laws and regulations that reduce AI-related risks.
- Data quality. Standards must be set to ensure the quality and security of the training dataset used to train AI models. The data must be accurate and fair so that the model that you train from the data works well and produces the desired output.
- Continuous monitoring. Once the model has moved into the post-production phase, it needs to be monitored continuously to ensure it is functioning as intended. Model governance ensures procedures to continuously train and monitor models as needed.
The future of AI governance
The future of AI governance relies on cooperation between governments, organizations and stakeholders. Its success depends on the development of comprehensive AI policies and regulations that protect the public while promoting innovation. Complying with data governance rules and privacy regulations, prioritizing safety, reliability and transparency is also important for the future of AI governance.
https://www.youtube.com/watch? v = bqdpuwvwpk4
Various companies are focusing on the future of AI governance. For example, in 2022, Microsoft released version 2 of the “Responsible AI Standard.” This is a guide to managing AI risks and incorporating ethical AI governance into your strategy. Other companies that have committed to implementing governance standards and guardrails include Amazon, Anthropic, Google, IBM, and Refraction.
US government agencies working in the region include the White House Science Policy Policy Office of the National Artificial Intelligence Initiative, launched in 2021. The National AI Advisory Committee was established in 2022 as part of a national AI initiative to advise the president on AI-related issues. Additionally, in collaboration with both the public and private sectors, the National Institute of Standards and Technology has developed a framework that recommends specific risk management approaches to those working with AI.
Some AI experts argue that there is a gap in the legal framework of AI accountability and integrity. In March 2023, technology leaders and AI experts such as Elon Musk and Steve Wozniak signed an open letter urging a temporary suspension of AI research and codification of legal regulations. In May, Openai CEO Sam Altman testified before Congress before urging AI regulations. Elon
Musk and Openai recently noticed in 2024 that Musk's Grok Generative AI was disputed about its location, environmental impact, and its operationality at ethical boundaries with fewer operations.
Other such companies are driving boundaries regarding AI governance. For example, Adobe updated its terms of service in 2024 to allow user-generated content to train machine learning software. After a massive backlash, Adobe has backtracked and renewed its Terms of Use agreement and pledged not to train AI on user content.
As AI adoption continues to increase and technology improves, companies are likely to continue to push the ethical boundaries associated with AI related to product delivery, and proper implementation of AI governance will become increasingly relevant. This means that AI fields are more likely to see more common calls for regulatory oversight. The White House blueprint for the AI Bill of Rights is a step in this direction, but there is a lack of specific details about how each principle should be implemented, and does not require organizations to follow it.
AI governance is the responsible regulation of artificial intelligence in the private and public sectors. What do you learn Companies need to know about AI regulations.



