Chiral metasurfaces are a powerful technique for controlling light and are essential for the development of advanced optical devices, and a team led by Davide Filippozzi at the Justus Liebig-University Giessen, along with Alexandre Mayer and Nicolas Roy from the University of Namur, are currently making significant advances in the design and performance of these nanostructures. Their study introduced a new optimization framework that combines the strengths of deep learning and evolutionary algorithms to overcome previous limitations in achieving both high chiral dichroism and strong reflectance. By comparing a neural network approach with a genetic algorithm, the research team demonstrated a doubling of chiral dichroism and revealed the importance of design parameters such as corner number and refractive index contrast, exemplified through simulations of GaP/air and PMMA/air metasurfaces. This research, which also includes contributions from Wei Fang from Zhejiang University and Arash Rahimi-Iman from Justus-Liebig-Universität Gießen, not only expands the number of viable designs considered, but also suggests the possibility of creating chiral mirrors with tailored spectral reflectance for polarization-selective light-matter interaction applications.
AI optimizes chiral metasurface design for increased responsiveness
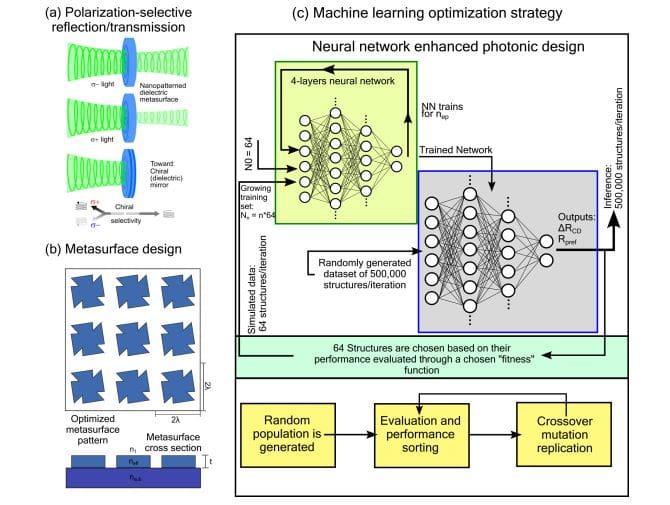
By combining deep learning and evolutionary algorithms, researchers have developed a powerful new method for designing chiral metasurfaces, nanoscale structures that manipulate light in unique ways. This innovative pipeline significantly improves both the design process and performance of these complex nanostructures, leading to improved optical properties. To speed up the optimization process and consider a wider range of designs, the team employed a neural network trained on data generated by rigorous electromagnetic simulations as a predictive model. This approach avoids the need for computationally expensive simulations for every potential structure, dramatically shortening the development cycle.
Key improvements include training a neural network to simultaneously predict both circularly polarized differential reflectance and reflectance preference, allowing for more accurate and robust optimization. The training process was further refined by dynamically adjusting the period based on the network's performance to prevent both overfitting and underfitting. To expand the training dataset without increasing computational cost, the team cleverly exploited the symmetry inherent in chiral structures, effectively doubling the data size through a geometric expansion technique. This method takes advantage of the relationships between enantiomers and mirrors the design to create new training samples. The combination of these techniques enables efficient and robust optimization of chiral metasurfaces, paving the way to advanced optical devices with tuned properties.
Double chiral dichroism with deep learning
Researchers have achieved significant progress in the design of chiral metasurfaces through a new optimization framework that combines deep learning and evolutionary algorithms. This study demonstrates that both the design process and performance of these complex nanostructures can be significantly improved, paving the way for advanced optical devices. The research team developed a pipeline that simultaneously optimizes for high chiral dichroism (a measure of a structure's ability to distinguish between left-handed and right-handed circularly polarized light) and high reflectance. Experiments revealed a doubling of chiral dichroism compared to previous designs, achieved through an improved neural network architecture and an improved fitness function used to evaluate the design.
This breakthrough was demonstrated using both gallium phosphide and polymethyl methacrylate materials, demonstrating the versatility of the optimization process. The structures were modeled at various geometric complexities while adhering to physical constraints regarding edge angles and intersections. The optimization process involved employing computational techniques to efficiently calculate light transmittance and reflectance, and using specialized software to simulate the behavior of the metasurface. Data augmentation techniques were implemented to enhance the robustness of the model and expand the design space. To complement the neural network, a genetic algorithm was also employed to operate on a population of potential structural designs. We suggest that this combined approach significantly increases the number of structures explored within limited computational resources and allows tuning the spectral reflectance of chiral mirrors, which can be applied to the study of polarization-selective light-matter interactions.
Chiral metasurface designed with machine learning
This study presents a significantly improved machine learning framework for designing chiral photonic metasurfaces. By combining sophisticated neural network architectures with evolutionary strategies, scientists have achieved structures that exhibit both high performance and efficient computational scaling. Results show a doubling of chiral dichroism compared to previous designs, highlighting the influence of both structural features and material selection. This study enables the creation of customized spectral reflectances and paves the way for practical fabrication of chiral mirrors and optical filters. These devices can be realized using a variety of lithographic techniques, providing flexibility in feature scale and fabrication methods. The authors highlight the efficiency of their optimized framework while being aware of the computational resources required for these simulations. Future research may focus on exploring a wider range of materials and geometries, further improving the design process, and expanding the potential applications of chiral metasurfaces in areas such as polarization-selective light-matter interaction studies.
👉 More information
🗞 Advances in machine learning optimization of chiral photonic metasurfaces: A comparative study of neural network and genetic algorithm approaches
🧠ArXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.13656